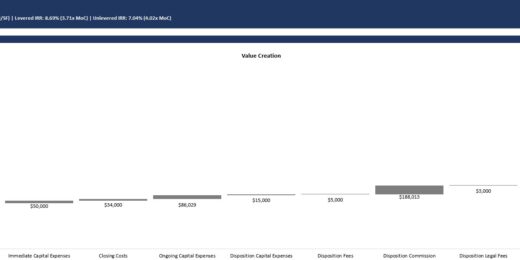
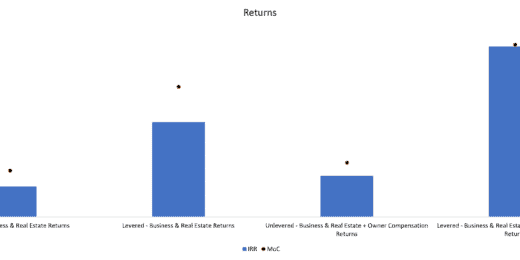
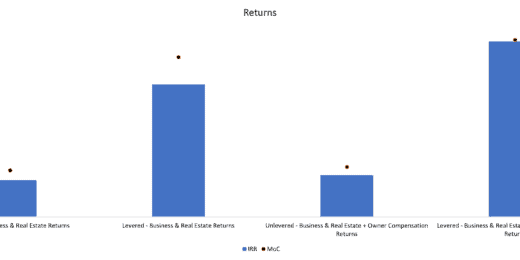
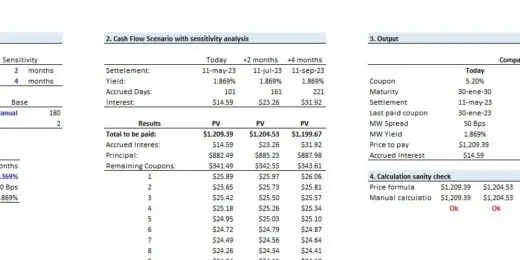
Bad Debt
Bookkeeping Agency Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Bookkeeping services…
B2C eCommerce Financial Model & Valuation Model
Tailored ecommerce financial model Model for startups. Forecast revenue, integrate…
Brewery Financial Model and Budget Control
This Excel model is an advanced, user-friendly financial planning tool…
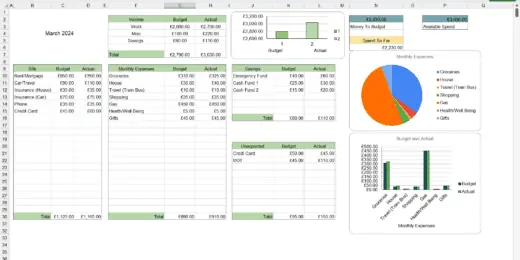
Ultimate Budget Spreadsheet, Budget Dashboard, Google Sheets, Excel
Ultimate Budget Spreadsheet, Budget Dashboard, in both Google Sheets and…
Coffee Shop Financial Plan and Budget Control
This Excel model is a highly adaptable and user-friendly tool…
Pro Financial Forecast – Dynamic and Advanced Financial Projections
Unleash the power of precise, customizable forecasting with Pro Financial…
Catering and Ballroom Rental Financial Model
This Excel model is a highly adaptable and user-friendly tool…
Rental Property (Airbnb – Real Estate) Financial Model
Powerful Real Estate Rental Property Financial Model for Informed Decision-Making,…
Nestle India Financial Model – Forecasting Until 2027
Unlock the power of decision-making with our Comprehensive Nestle India…
Blue Ammonia using Natural Gas – 3 Statements, Cash Waterfall & NPV/IRR Analysis
An integrated and comprehensive Blue Ammonia Production Plant Model that…
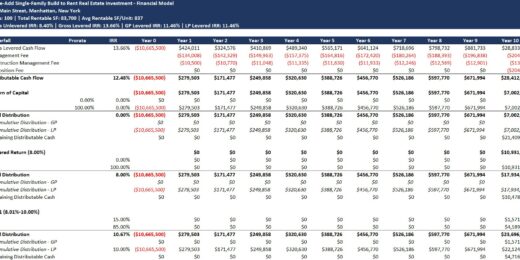
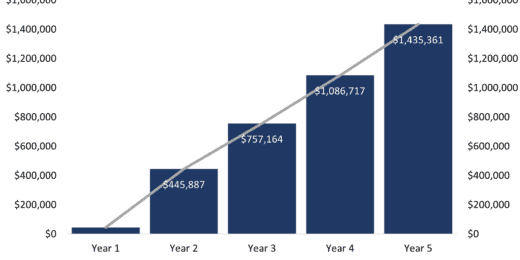
Value-Add Single-Family (SFR) Build to Rent (B2R) Real Estate Investment Model with Waterfall
A financial model to help calculate and analyze the pro…
eCommerce Monthly 3-Statement Business Plan with Return Calculations
A model to prepare and analyze a start-up or existing…
Software as a Service (SaaS) Monthly 3-Statement Business Plan with Return Calculations
Pro Forma Models created this model to prepare and analyze…
Mobile Applications (App) Monthly 3-Statement Business Plan with Return Calculation
Pro Forma Models created this model to prepare and analyze…
Principal Residence Real Estate Investment Model
This Pro Forma Model is designed to analyze Principal Residence…
Real Estate Brokerage Business Plan with Return Calculation
Pro Forma Models created this model to analyze the financial return…
Property Manager Plan with Return Calculations & M&A Model
Pro Forma Models created this model to analyze the financial return…
Dynamic Franchise Business Plan – 3 Statement Model with DCF & Returns
Pro Forma Models created this model to analyze the financial…
Bond, Loan or Note Make Whole Calculator
The model is designed to evaluate a make-whole calculator for…
Hotel Real Estate Investment Model Template
Pro Forma Models created this financial model to calculate and…
Core Multi-Family (Apartment) Real Estate Investment Model with Waterfall
Pro Forma Models created this financial model to calculate and…
Real Estate – Self Storage Acquisition Model
This template is an Institutional-Quality excel-based analysis tool for a…
Real Estate Investment Model Template with Waterfall & Catch Up
The waterfall model includes a dynamic catch up. This model…
Wholesale Business 3 Statement Model with Returns Calculation
This model can be used to analyze the financial return…
Real Estate Investment Screening Model – Levered IRR, Unlevered IRR, Cap Rate, DSCR, and More
This model can be used to quickly (5 minutes if…
Start-Up Business 3 Statement Model with Returns Calculation
This model can be used to analyze the financial return…
Single Tenant Property Investment Valuation & Return Model
This model can be used to analyze the financial return…
Dynamic Single-Family Home Investment Analysis Model
This is a highly dynamic single-family home investment analysis model.…
Self Storage Financial Model (Construction, Operations & Exit)
Considering investing in a self-storage facility? This might be an…
Accounts Receivable and Accounts Payable / Invoice Tracking – Aging Report Template
User friendly template to monitor Accounts Receivable & Accounts Payable…
Credit Control & Debt Recovery Procedures
Debt Collection is the execution of functions necessary to collect…
Banking Model with 3 Statements – Dividend Discount (DDM) and Net Asset Value (NAV) based Valuation
Financial model that performs a DDM & NAV based valuation…
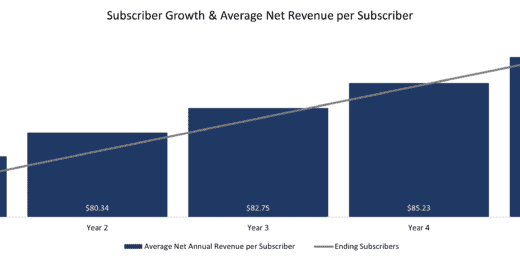
Youtube Content Creator Financial Model Excel Template (Fully-Vetted and Ready-to-Use)
Fully-Vetted Comprehensive Youtube Content Creator Financial Model + Video Series…
Commercial Real Estate – Lease or Sell Quarterly Excel Model Template
Commercial Real Estate - Lease or Sell Quarterly Excel Model…
Bad Debt Reserve Calculator
Spreadsheet to calculate general accounts receivable reserve based on a…
Smartly Managing Bad Debt Expenses

In the contemporary business landscape, bad debt expenses are a formidable challenge that can significantly impact companies' financial health and operational viability. This phenomenon occurs when clients or customers fail to meet payment obligations, leading to unrecoverable funds expected as revenue. The effects of bad debt expenses extend beyond mere financial loss; they can erode profit margins, distort cash flow projections, and, in severe cases, jeopardize the sustainability of the business.
As companies navigate the complexities of market dynamics, managing bad debts and knowing how to write off bad debt becomes a critical component of their strategic financial planning, necessitating a deep understanding of its potential repercussions on their overall business health. Through the lens of this article, we will explore innovative methods and best practices for managing bad debt, offering insights into how companies can enhance their financial resilience.
Understanding Bad Debt Expenses
Bad debt refers to outstanding balances owed to a business no longer deemed recoverable and must be written off as a loss. This situation arises when customers who have purchased goods or services on credit cannot pay the amount they owe. Recognizing bad debts on the financial statements is essential as it provides a more accurate picture of the company's financial health. Bad debts are considered an expense and are part of the cost of doing business, especially for companies that extend credit to their customers.
Businesses incur bad debts due to a variety of reasons:
- Administrative Errors: Mistakes such as incorrect billing, failing to update customer contact information, or not correctly tracking payments can lead to difficulties in collecting payments. These administrative oversights might result in invoices being ignored or disputed by the customer.
- Customer Insolvency: If a customer goes bankrupt or faces severe financial difficulties, they may become incapable of settling their debts. It is one of the most common reasons for bad debts, as the customer's lack of funds makes it impossible for the business to recover the owed amount.
- Disputes: Disagreements over the delivered goods or services can lead to non-payment. Customers may refuse to pay if they believe what they received was not as promised or contracted, leading to unresolved disputes and eventual write-offs.
- Fraud: In some cases, bad debts can occur due to fraudulent activities, where customers intentionally deceive the business with no intention of paying for the goods or services received.
- Poor Credit Policies: A business must have lenient credit policies or adequately assess a customer's creditworthiness before extending credit to avoid ending up with more defaulting customers. Effective credit management involves setting clear criteria for who is eligible for credit and under what terms.
A high bad debt rate typically indicates that a business should aim to be more effective in managing its credit and collections process. This inefficiency can stem from a lack of stringent credit assessment procedures, inadequate follow-up on overdue accounts, or poor customer selection. High levels of bad debt affect a company's profitability, cash flow, and operational efficiency.

The Bad Debt Expense Accounting Entry
A bad debt expense accounting entry involves understanding how it affects a company's financial statements and its position regarding debit or credit, its classification as an operating expense, and where it is recorded on the income statement.
Is Bad Debt Expense a Debit or Credit?
In accounting, bad debt expense is recorded as a debit. It is because accounting entries follow the double-entry system, where each transaction must have both a debit and a credit to keep the accounting equation balanced. When a company recognizes bad debt expense, it increases the expense account, which reduces net income on the income statement. The corresponding credit entry is typically made to an allowance for doubtful accounts, a contra-asset account that reduces the total accounts receivable balance on the balance sheet.

Is Bad Debt Expense an Operating Expense?
Yes, bad debt expense is considered an operating expense. It is directly related to a business's sales and credit policies and impacts the operating income. Operating expenses are necessary costs for running day-to-day operations and generating revenue. Since bad debts arise from credit sales that are part of the normal operations of a business, they are categorized under operating expenses.
A bad debt expense accounting entry is recorded under Sales, General, and Administrative Expenses (SG&A) on the income statement. It represents the portion of receivables that a company estimates it cannot collect. This estimation is crucial for companies that sell goods or services on credit, as it reflects a more accurate picture of the revenue that will actually be realized.
How to Write Off Bad Debt
Writing off bad debt is critical for accurate financial reporting. It also allows businesses to reflect their financial health correctly. Recognizing these uncollectible accounts ensures that a business's financial statements only show revenue from transactions likely to result in actual cash inflows. This accuracy is essential for effective financial planning and analysis and for maintaining the trust of investors and creditors. Businesses can use one of two primary methods on how to write off bad debt: the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and the Direct Write-Off Method.
Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Method
The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts Method estimates the bad debt from accounts receivable during a specific period. This estimation is based on historical data, industry averages, and the current economic climate. A contra-asset account, known as the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts, represents the estimated amount of receivables expected to go uncollected. The business does not immediately write off the bad debt when an account is deemed uncollectible. Instead, it makes an adjusting entry that debits the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts and credits Accounts Receivable. This method smooths the expense recognition over time and reflects a more accurate view of the business's financial condition. The Allowance for Doubtful Accounts is a more conservative approach that anticipates future bad debts and allocates a portion of accounts receivable as uncollectible in advance.
Direct Write-Off Method
The Direct Write-Off Method removes the bad debt from the accounts only after it becomes clear that the debtor cannot pay. It waits until a specific account is deemed uncollectible before writing it off. When it becomes apparent that a debtor will not pay, the business directly writes off the bad debt by debiting Bad Debt Expenses and crediting Accounts Receivable for the amount of the uncollectible account. This method can result in a less consistent match of expenses with revenues because bad debt expenses may be recognized in a different period from when the related revenues were earned. Although more straightforward, the Direct Write-Off Method can distort a company's financial results and is not accepted under Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) for financial reporting purposes. However, it is still used for tax purposes in some jurisdictions.
Understanding and choosing the appropriate method of how to write off bad debt is essential for maintaining accurate financial records and ensuring the business portrays a true and fair view of its financial performance and position.

Strategies to Minimize Bad Debts
The specter of bad debts looms large, posing a formidable challenge to the stability and growth of businesses. Managing and minimizing bad debts is crucial for maintaining a healthy cash flow and ensuring long-term success. Let us delve into the strategies that can help companies safeguard against the financial strain caused by bad debts. To effectively manage and minimize bad debts, businesses can adopt several strategies:
Automate Collections
Automating collections involves using software to manage and track the billing and collections process. This strategy can significantly reduce the time and effort required to follow up on late payments, as automated reminders can be sent to customers at pre-defined intervals. Automation helps identify overdue accounts faster, enabling timely intervention before accounts become significantly past due. This approach streamlines the collections process and maintains consistent customer communication regarding their payment status.
Credit Check New Customers
Performing credit checks on new customers before extending credit is crucial in minimizing bad debts. By assessing the creditworthiness of potential customers, businesses can identify any financial risks ahead of time. This information can guide decisions on extending credit and on what terms. Credit checks help segregate customers based on their credit risk, allowing businesses to apply more stringent payment terms for higher-risk customers and reducing the likelihood of bad debts.
Factoring
Factoring is a financial strategy businesses use to improve their cash flow and minimize the risk associated with bad debt. By selling their accounts receivable (invoices) to a factoring company at a discount, typically around 5% less than the nominal value, businesses can receive immediate cash, which is crucial for maintaining operations and investing in growth opportunities. This arrangement transfers the risk of collecting the receivables from the original business to the factoring company. Consequently, the business avoids the hassles and uncertainties of managing receivables and chasing up late payments, ensuring they receive 95% of the invoice value upfront. This practice is particularly beneficial for companies looking to mitigate credit risk and enhance financial stability without dedicating internal resources to collections.
Fix Disputes Quickly
Disputes over invoices can delay payments, increasing the risk of bad debts. Resolving these disputes quickly is essential to maintaining cash flow. This strategy involves a straightforward process for addressing and resolving disputes efficiently, ensuring that any issues are corrected promptly to facilitate faster payment. Quick dispute resolution not only helps in recovering dues more swiftly but also aids in preserving good customer relationships by demonstrating a commitment to customer service.
Offer Flexible Payment Options
Providing customers with flexible payment options can also help in minimizing bad debts. Flexibility might include various payment methods, installment plans, or adjustments to payment terms. Such accommodations can make it easier for customers to make payments according to their financial situation, reducing the likelihood of missed or late payments. Flexible payment options can also enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, which are beneficial for long-term business success.
Regularly Follow Up on Late Payments
Consistent follow-up on late payments is critical for minimizing bad debts. It means regularly contacting customers with overdue invoices to remind them of their payment obligations. Follow-ups can be conducted through various communication channels, such as emails, phone calls, or letters. Regular contact emphasizes the importance of timely payments and allows businesses to identify and address any potential issues that may be causing payment delays.
Send Invoices and Statements Promptly
Promptly sending invoices and statements to customers is fundamental to ensuring timely payments. Invoices should clearly outline the payment due date, amount, and instructions to ensure everything is clear. Sending invoices immediately after a product or service is delivered increases the likelihood of receiving payments on time, as the transaction remains fresh in the customer's mind. Timely billing reinforces the expectation of prompt payment, reducing the window for payment delays.
Set Clear Payment Terms
Setting clear payment terms with customers before engaging in business transactions is essential for minimizing bad debts. Clear terms include specifying due dates, late payment penalties, and discounts for early payments. Such clarity ensures that both parties understand the payment expectations, reducing misunderstandings and disputes. Clear payment terms also provide a legal framework for enforcing collections if necessary, further protecting the business from potential bad debts.
Together, these strategies form a comprehensive approach to minimizing bad debts. Implementing these practices can significantly improve a business's financial health by enhancing cash flow and reducing the incidence of unpaid invoices.

Mitigate Bad Debt with Strategic Financial Modeling
Managing bad debts effectively is crucial for businesses to maintain healthy cash flows, ensure financial stability, and sustain long-term growth. Bad debts occur when customers fail to pay back what they owe, leading to lost revenue and potentially impairing a company's ability to invest, pay its own debts, or even manage operational expenses. This risk is especially pronounced for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that operate with tighter margins and may have less capacity to absorb financial shocks. By prioritizing the management of bad debts, businesses can protect their bottom line, improve their credit rating, and foster stronger relationships with their customers by avoiding aggressive collection tactics.
Businesses can adopt several proactive strategies to reduce the incidence of bad debts. Automating the collections process can help in timely follow-ups and reduce the manual effort of chasing payments. Performing thorough credit checks before extending credit can filter out high-risk customers. Offering flexible payment options can also assist customers in managing their finances better, thereby increasing the likelihood of full repayment. Moreover, setting clear payment terms upfront can prevent misunderstandings and disputes, often leading to delayed payments. Together, these strategies create a comprehensive approach to managing credit risk and minimizing the financial impact of bad debts on the business.
Incorporating financial model templates into a business's financial planning and analysis can further mitigate the risk of bad debts. Such templates help in forecasting cash flows, assessing the impact of potential bad debts on the business's financial health, and setting aside adequate provisions for doubtful debts. By integrating risk assessments and credit management strategies into their financial models, companies can anticipate and prepare for the potential financial impact of bad debts. This proactive financial planning enables companies to maintain operational resilience, make informed decisions about credit policies, and ultimately support sustainable growth despite the challenges posed by bad debts.