Valuation
Startup Company Financial Model – Dynamic 3 Statement Financial Projections up to 8-Years
Highly Dynamic and Easy-to-Navigate Excel Financial Projections Model that allows…
Advanced Financial Model – Dynamic 3 Statement 10-Year Financial Model with DCF Valuation
Advanced, Dynamic and Easy-to-Use Excel Financial Projections Model that allows…
Parcel Locker Network Business Financial Model (10+ Yrs. DCF and Valuation)
The Parcel Locker Network Business Financial Model is a comprehensive…
Dental Imaging Center Financial Model
The Dental Imaging Center financial model is a comprehensive tool…
Mobile Imaging Center Financial Model
This Excel model facilitates mobile imaging services by providing equipment…
Private Aircraft Rental Business Financial Model
"The Private Aircraft Rental business financial model is a versatile…
B2B SaaS FInancial Model & Valuation Template
Unlock your B2B SaaS venture's full potential with our B2B…
VC Startup Portfolio Financial Forecasting Model
Elevate your venture capital strategy with the VC Startup Portfolio…
Beginner Commercial Property Modelling Tool
"Beginners Commercial Property Modelling Tool," a resource for developers embarking…
Fintech Mobile App Financial Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Fintech Mobile…
Indoor Golf Centre Finance Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Indoor Golf…
Manufacturing Start up Feasibility Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for forecasting and tracking…
B2B Services Company Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking B2B Services…
Medical Spa (MediSpa) Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Medical Spa…
Physiotherapy Clinic Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Physiotherapy Clinic…
Virtual Reality Software Company Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Virtual Reality…
Budget vs Actual Forecasts 5 Years Excel Template
MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking budget finances. Can be used…
3 Statement 5 Year SAAS HR Software Development Company Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking SAAS HR…
Car Dealership Financial Model and Valuation – Financial Projections
Welcome to the Car Dealership Company Financial Model and Valuation,…
Hospitality (Hotel) Financial Model and Valuation – 10-year Projections
Welcome to the Hospitality (Hotel) Company Financial Model and Valuation,…
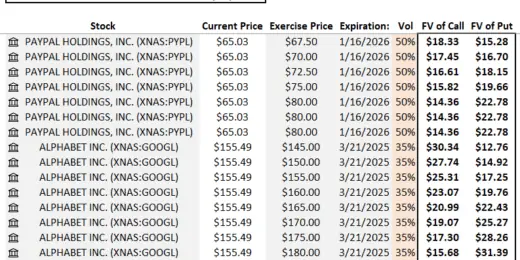
Equity Options Fair Value Calculator (Black-Scholes)
The Equity Options Fair Value Calculator (Black-Scholes) is your go-to…
B2C eCommerce Financial Model & Valuation Model
Tailored ecommerce financial model Model for startups. Forecast revenue, integrate…
Construction Machinery Rental Company Financial Model
Discover the key to financial planning in the construction machinery…
Business Valuation Spreadsheet
This file enables you to effortlessly compute the Estimated Business…
Healthcare – Hospital – Financial Model and Valuation (10-year Forecast)
Welcome to the Healthcare (Hospital) Company Financial Model and Valuation,…
Motorboat Rental Business Financial Model
Dive into the heart of financial planning with our Motorboat…
AgroTech Services Financial Model (10+ Yrs. DCF and Valuation)
The AgroTech Services Financial Model with DCF (Discounted Cash Flow)…
Crypto Token Valuation Model
A cutting-edge crypto token valuation model, designed to provide comprehensive…
Complete Private Equity (LBO) Financial Model
This is a professional financial model which performs a thorough…
Urban Micro-Mobility Services Financial Model (10+ Yrs. DCF and Valuation)
The Urban Micro-Mobility Services Financial Model with DCF (Discounted Cash…
Coffee Shop Financial Plan and Budget Control
This Excel model is a highly adaptable and user-friendly tool…
Crane Truck Rental Company Financial Model
Step into the world of crane rental business success with…
Telehealth Services Company Financial Model (10+ Yrs. DCF and Valuation)
The Telehealth Services Company Financial Model with a 10+ Years…
Ship Management Business 5-Year 3 Statement Financial Projection Model
5 year rolling financial projection Excel model for a startup…
Online Tutoring Services Financial Model (10+ Yrs DCF and Valuation)
The Online Tutoring Services Financial Model is a comprehensive tool…
Pro Financial Forecast – Dynamic and Advanced Financial Projections
Unleash the power of precise, customizable forecasting with Pro Financial…
Industrial Warehouse Business 10-Year 3 Statement Financial Projection Model
10 year rolling financial projection Excel model for a startup…
Cleaning Service Pro Forma Template (Commercial / Residential)
A pro forma template for any home service or general…
Oil & Gas Financial Model – DCF and NAV Valuation (5+ Yrs.)
The Oil and Gas financial model with DCF (Discounted Cash…
CPG Company Financial Model and Valuation
Discover the CPG Company Financial Model and Valuation, an essential…
eCommerce | Online Retail Financial Model and Valuation
Discover the eCommerce - Online Retail Company Financial Model and…
Self Storage Business 10-Year 3 Statement Financial Projection Model
10 year rolling financial projection Excel model for a startup…
Dog Grooming Services Financial Model (10+ Yrs DCF and Valuation)
The Dog Grooming Services financial model is a comprehensive tool…
Ship-to-Ship Fuel Bunkering 5-Year 3 Statement Financial Projection Model
5-year rolling 3 statement financial projection with a monthly timeline…
Buy Now Pay Later DCF Model & Valuation (10 Year DCF Model)
The Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) Company financial model is…
Care Home Business 10-Year 3 Statement Financial Projection Model
10 year rolling financial projection Excel model for a multi…
Sailboat Rental Business Financial Model
This comprehensive 10-year monthly Excel template offers an ideal basis…
Hotel Complex – Financial Model (5 Yrs. DCF and Valuation)
The Hotel Complex financial model is a comprehensive tool designed…
Comprehensive Oil & Gas Financial Model
Comprehensive financial model for an oil & gas company. Flexible…
Leasing Company 5-Year Financial Projection Model
5 year rolling financial projection Excel model for a leasing…
Weighted Average Cost of Capital (WACC) Calculator
This Excel template has a comprehensive WACC calculator. It allows…
Start-up Manufacturing Financial Projection and Budget Control – Excel & Google Sheets
The financial model is an essential tool that enables owners…
Financial Modeling Mastery Bundle: Diverse Insights for Informed Decision-Making
Unlock financial expertise with our 'Diverse Insights Bundle.' Seven meticulously…
Valuation Approaches
Valuation, as we already know, is the process of determining the current value of an asset or a business. From conducting a valuation for tangible or intangible assets to valuing liabilities such as bonds, etc. But one must remember that in valuation, the resulting value is subjective since it’s mostly an estimation and will vary accordingly depending on who’s conducting the valuation of an asset or a business.
In Valuation, there are three common terms that you’ll encounter as to describe the value of an asset or liability.
- Market Value – also knowns as Open Market Valuation (OMV), this is the value perceived by the open market
- Fair Value – a rational estimate of what could be the value of an asset determined by an evaluation expert
- Intrinsic Value – also known as Fundamental Value, is the current value of an asset determined by conducting a fundamental analysis without having to refer to its current market value
Business Valuation is a specific kind of valuation where instead of assets or liabilities, it’s more focused on determining the value of businesses and related entities. This is to determine the economic value of a business. Basically, business valuation is conducted when a business wants to sell all or a part of their current operations, or in some cases for merging and acquiring other businesses.
Business valuations can be done in a number of ways, the commonly used approaches are to evaluate the business’ health of cash flows, timings of cash flows, net assets, potential earnings, and costs. Generally, the resulting value will differ from the buyer’s and seller’s points of view. Due to their differing goals, the buyer mostly focuses on the value he pays. While for the seller, it’s what the business is worth, thus, ensuring that they won’t sell below that value.
Of course, a single valuation model will not always result in a fair value, thus to arrive at a fair value range, there are three broad valuation approaches that one can use.
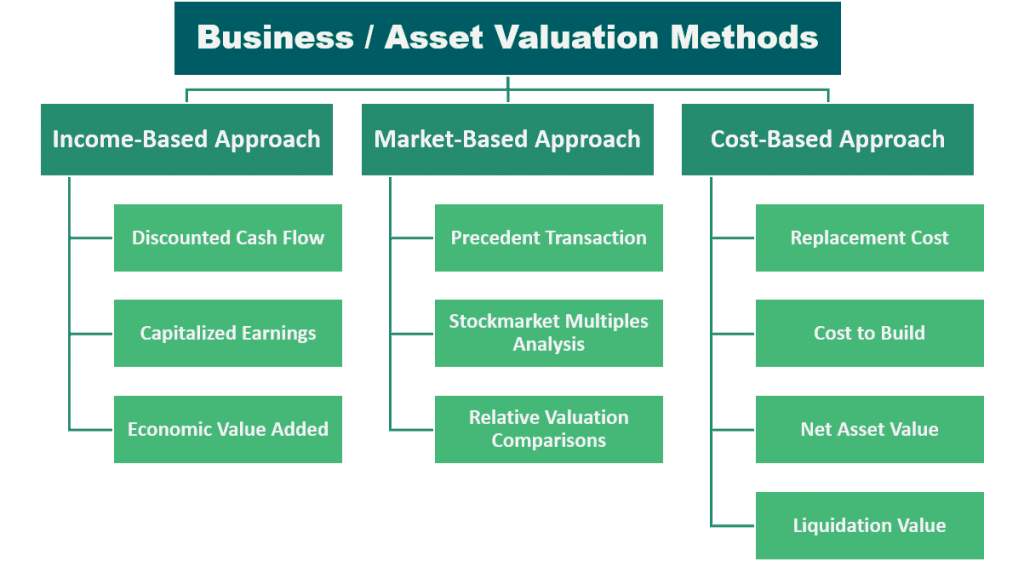
Income-Based Approach
This is one of the three popular approaches to valuation, especially for income-producing properties. This approach values a business based on its past, current, or forecasted cash flow and used for exploring the intrinsic value of any business by evaluating the cash flows, NPV, equity method, and economic profit model. The key objective of the income-based approach is to determine the value of a business that will result in an economic benefit to the parties involved.
Of course, there are pros and cons to using the income approach. One of the advantages when using this approach is its flexibility in addressing businesses or assets in their different stages of life-cycle since it factors different assumptions over the projected period. Though it is considered powerful and effective unlike the other approaches, it doesn’t need to rely on any historical financials. So, it is very convenient for small businesses or startups that don’t have enough past transactions.
However, this approach is dependent on the assumptions on the future projections, it tends to be subjective, especially if the assumptions are not tested. There is a great risk of being inaccurate and biased since it, after all, makes use of estimated figures which can be manipulated according to one’s preference. The resulting value is also highly sensitive due to different estimates of growth rate and required rate of return, thus, the appraiser needs to provide inputs that are realistic and fair. It is clear that the income-based approach valuation can be a bit more complex compared to the other approaches therefore, it requires more time for its implementation.
The following are the methods that make use of the income-based approach:
- Discounted Cash Flow – This method is used to value a business by basing it on its future cash flows which are then discounted to the present value of the business. Basically, you need to make an estimate of the future cash flows and estimate also a realistic discount rate after undergoing different assumptions that will affect the value such as certain risks and interest rates. Then, using the derived estimates, you will calculate to come up with an assumed present value of the future cash flows.
- Capitalization of Earnings – This method is used to value a business by discounting its future earnings and dividing them by the capitalization rate. Using this method will also be beneficial in determining the potential risks and return of buying a business. To determine the capitalization rate, one will need significant know-how of the business and industry. Once all variables needed are known, you can simply use the formula: Capitalization rate = Operating Income/Purchase Price.
- Economic Value Added – EVA or also known as Economic Profit is another method under the income-based approach due to its nature of valuing a business based on its residual wealth which is calculated by deducting the cost of capital to its operating project, then adjusted for taxes on a cash basis. Basically, by using this method, you will be able to determine a business’s financial performance or simply put, to show that the business is producing value from the funds invested in it.
Market-Based Approach
The next known approach to valuation is the market-based approach. It is used to determine the value of a business, intangible asset, business ownership interest, or security, by taking into account the market prices of assets or businesses that are comparable and were sold or still on the market. Thus, when conducting a valuation, there will be adjustments made based on the historical or present prices of the assets or business accordingly.
The market-based approach is a handy approach when capturing the market sentiment, considering the peers. It helps determine the value of a business or asset by doing a comparison to historic sales of similar businesses. In this method, it relies on pricing multiples to determine if there’s relevance between the economic value and potential selling price of a business.
Just like the income-based approach, the market-based approach has its own advantages and disadvantages. First off, since it is a straightforward method, it only involves simple calculations. This means it is easy to understand and more honest since it uses figures or data which is real and public. Thus, no need for guessing or making any estimations which makes the market approach not dependent on subjective projections. But, this means that it is less flexible compared to the other approaches. Some opportunities to earn or save more might be lost without checking the future value of a business after all. Another one of its disadvantages is, it also raised problems such as not having enough data available or if the data is good enough to use. One would need an experienced expert with expansive know-how in the industry to try and resolve those issues.
There are three methods that make use of the market-based approach:
- Precedent Transaction Analysis – This is a valuation method where the value is derived from the historical price value of a comparable business. As a market-based approach, it heavily relies on public information to arrive at a reasonable estimate of multiples or premiums from other buyers or sellers for a publicly traded business. This method is commonly used by analysts for mergers and acquisitions.
- Stockmarket Multiples Analysis – This valuation method is less known but works the same as Quoted Comparable Company Analysis where the data used to compare prices is derived from the stock market. This method is usually used for valuing listed businesses by comparing multiples such as EV/Sales, EV/EBITDA, EV/EBIT, and P/E.
- Relative Valuation Comparisons – By using this method, you’ll be able to determine the value of a business by conducting a market analysis regarding the pricing of its competitors or comparable business. This valuation method will require one to do a lot of research and comparing of prices to get the ideal price that would help with earning back more (for those who sold their assets) or saving up money (for those interested buyers). Mostly, this method is to determine whether you won’t go over or under the current pricing range. Another thing to take note of is that this valuation method is more industry-specific (e.g. value per room - hotels, value per sqm - real estate).
Cost-Based Approach
The last approach, the cost-based approach, is a valuation method that values a business based on the balance sheet and is generally known as the property valuation approach. This approach focuses on determining the net asset value (NAV) or the fair market value (FMV) out of the total assets, then subtracted by the total existing liabilities resulting in the would-be cost to re-create the business. In other words, it takes the net difference between the value of its assets and liabilities. Generally, it is used to value businesses based on the market value of assets, cost to build, replacement costs, and liquidation value of the assets.
This valuation method is usually used in certain cases such as replacing the business building or determining an estimated value of an individual tangible asset or intangible asset. Since the data needed to calculate is available by just referring to the balance sheet, finding the total value is easier and simpler compared to the other approaches, but then again it only focuses on finding the value of cost to be expended rather than determining the total value of a business's future earnings to determine the value of a business.
There are four methods that use the cost-based approach valuation:
- Replacement Cost – A business valuation method where you value a business by considering the replacement cost instead of the liquidation value deducted by the total liabilities to determine the value of a business. The replacement cost is usually higher than the book value due to depreciation not being accounted for. Another way of calling this method is the replacement value method.
- Cost to Build – A valuation method to estimate the value of an asset or business by considering the cost incurred to build and to make it fully operational. Basically, it’s a method focused only on the cost expended to determine the value of an asset or business. This valuation method is more ideal for real estate to determine the price a buyer should pay which should be equal to the cost to build the same property.
- Net Asset Value – This method is used to determine the value of a business by estimating the current value based on the existing assets and liabilities of a business. In cases where a solvent company shuts down, decided to sell off all assets, and settling its liabilities, the leftover cash would then serve as the current floor value of the business. Hence, the name net asset value represents the net value of an asset or business. The formula to arrive at the resulting net asset value is by taking the total value of an asset or business minus the total value of its liabilities.
- Liquidation Value – This valuation method is applicable only to businesses that are out or about to go out of business (e.g. bankruptcies, workouts, insolvency, etc.). If a business qualifies either of the two, the total value of a business is then determined via taking the total worth of the business's physical assets such as real estate, fixtures, equipment, and inventory. Take note that the intangible assets aren’t counted in determining the liquidation value which is why it is typically lower than the fair market value.
As you noticed, the income-based approach is mentioned first, the market-based approach is second, and lastly, the cost-based approach. It is placed that way since that’s usually the systematic way of determining the value of an asset or business. The first on valuing a business is to calculate the past, present, and future income of the business to derive the potential value of a business. Then after getting that result, the next step would be to compare the value derived to comparable businesses in the market. This is to check if the resulting value is a fair value and not over or under the acceptable range of prices based on the prices of comparable businesses. Lastly, to further check the estimated value of the business, the last approach is to check the total value of existing assets minus the liabilities. In conclusion, all three approaches have their own advantages and disadvantages but it is also clear to see that each approach are somewhat connected and have their own edges that differentiates them from the other approaches.
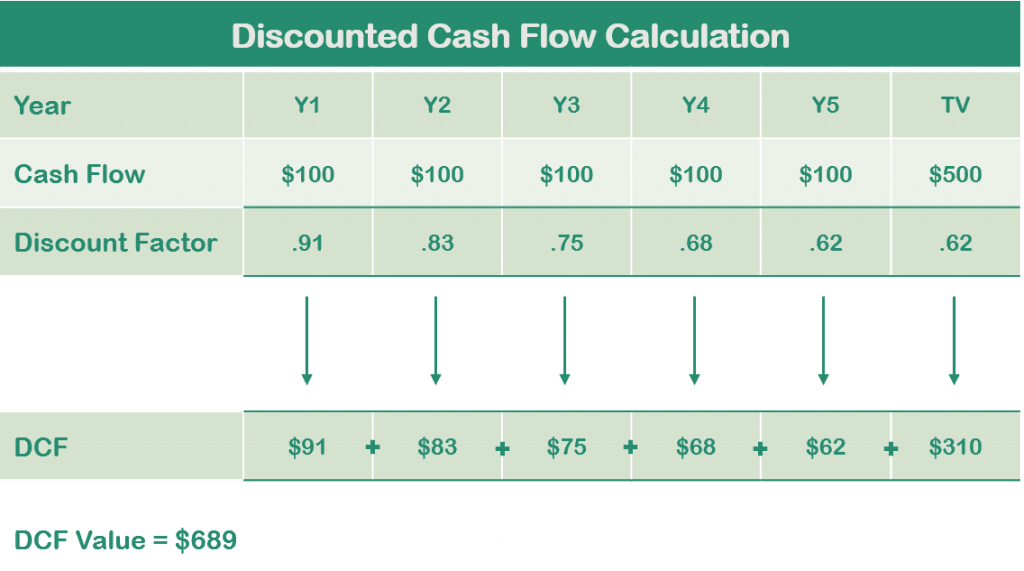
Discounted Cash Flow Valuation Method – The Most Used Valuation Method
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) is a valuation method that uses the income approach to determine the value of an asset or business. It is usually used to make an estimate on how attractive an investment opportunity is. Hence, it is quite popular and most used by interested parties to conduct the valuation. This method analyzes the future cash flow projections and discounts them with the required annual rate to determine the present estimated value of an entity. The value derived is then used to evaluate if the investment is potentially feasible or profitable.
The formula is as follows:
DCF = [CF1 / (1+r)1] + [CF2 / (1+r)2] + ... + [CFn / (1+r)n]
CF = Cash Flow
n = year
r= discount rate (Weighted Average Cost of Capital)
To further understand how it is calculated, see below illustration as an example.
Uses of Valuation
Valuation covers a wide range of uses such as:
- Averting Shareholder Disputes: Oftentimes, there are cases when a business fails, which will lead to a dilemma on how to break up the assets accordingly. So, conducting a valuation will help avert disputes between the shareholders.
- Mergers, Acquisitions, and Sales: Valuation is very critical to these tasks. The model will be used as a tool to negotiate for either mergers, acquisitions, or sale of assets, thus, both interested parties will be satisfied as they come up with the best fair market price.
- Buy-Sell Agreements: Valuation is usually conducted when transferring equity between partners or shareholders.
- Purchase Price Allocation: The valuation will serve as a report about all the business’ assets and liabilities to determine the tangible and intangible assets.
- Financing: Usually, to gain the interest of investors, they would require you to submit a report about the value of your business as proof that your business is worth investing in. Thus, a valuation is done to appraise your business. This also applies when obtaining a loan and other ways to raise financing.
- Employee Stock Participation Scheme: Is also known as the Employee Stock Purchase Plan (ESPP) where you give the employees an opportunity to purchase stock shares to be more devoted to the business.
There are many other current cases that valuation is needed so it is undeniable that valuation is significant in many ways.
Valuation Model Templates in Excel
Usually, it is recommended to ask for help when doing a valuation since it is, after all, you want to get most of it when selling a business or settle with a great investment when acquiring or merging with other businesses. An appraiser or an expert in valuation models is needed typically, but this doesn’t mean that one can’t do it themselves. With the existing tools available nowadays, conducting a valuation can be done without having to go through different processes especially when starting from scratch. Therefore, instead of spending high costs for professional services or spending too much time figuring it out on your own, making use of valuation model templates in Excel is a much better choice.
If you are looking for valuation model templates in Excel, then you can check out our list above and see if there are model templates that fit your specifications. The available models are ready-made and user-friendly with clear transparency so that when you edit them accordingly, you won’t have to spend a lot of time figuring how the values came about. The valuation model templates in Excel are made by skilled experts in financial modeling with extensive experience and industry know-how, thus, you can rest assured that the valuation models are professional looking and designed accordingly for different applications.
Here is a list of financial model templates that include a Valuation:
No Downloads found