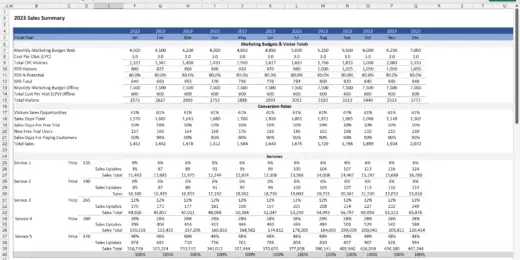
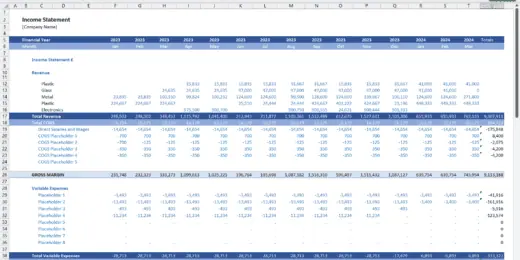
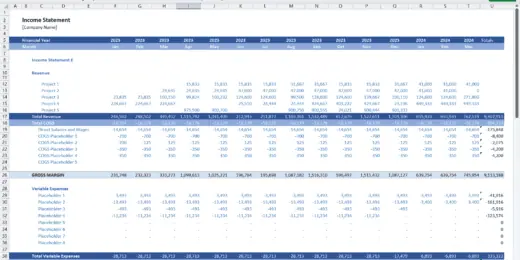
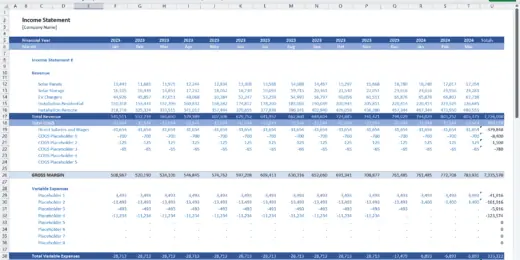
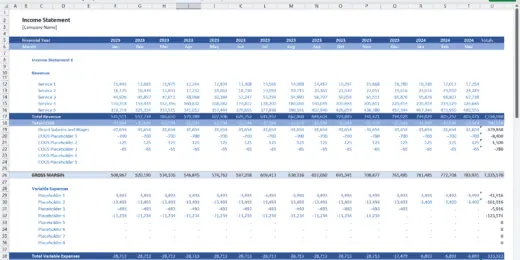
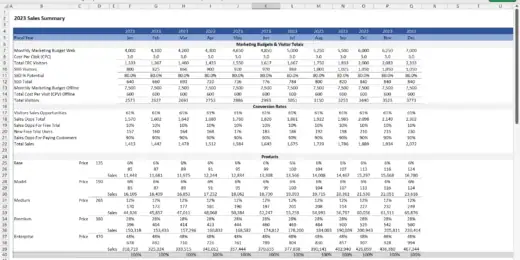
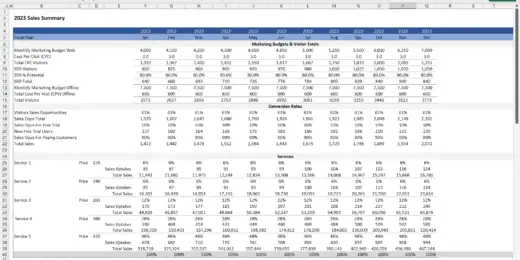
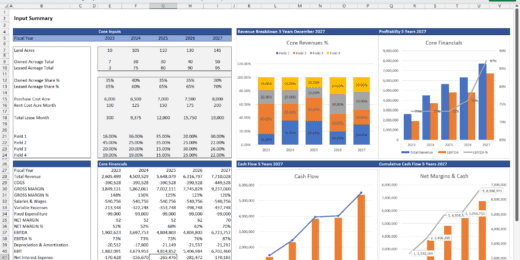
Financial Statements
EV Charging Station Finance Model
Provides a comprehensive analysis of the financial viability and potential…
Startup Company Financial Model – Dynamic 3 Statement Financial Projections up to 8-Years
Highly Dynamic and Easy-to-Navigate Excel Financial Projections Model that allows…
Advanced Financial Model – Dynamic 3 Statement 10-Year Financial Model with DCF Valuation
Advanced, Dynamic and Easy-to-Use Excel Financial Projections Model that allows…
Veterinary Imaging Center Financial Model
The Veterinary Imaging Center financial model is designed to analyze…
Parcel Locker Network Business Financial Model (10+ Yrs. DCF and Valuation)
The Parcel Locker Network Business Financial Model is a comprehensive…
Dental Imaging Center Financial Model
The Dental Imaging Center financial model is a comprehensive tool…
Diagnostic and Analysis Center Financial Model
It is excel financial model for financial forecasting of a…
Diagnostic Collection Center Financial Model
It is financial model for diagnostic collection center whose phlebotomists…
Mobile Imaging Center Financial Model
This Excel model facilitates mobile imaging services by providing equipment…
Private Aircraft Rental Business Financial Model
"The Private Aircraft Rental business financial model is a versatile…
Radiology Center Financial Model
The Radiology Center financial model is a comprehensive and versatile…
Biomethane Producer Financial Model (Renewable Natural Gas)
Create a detailed pro forma with this biogas financial model.…
Fintech Mobile App Financial Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Fintech Mobile…
Indoor Golf Centre Finance Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Indoor Golf…
Animal Feed Mill – 10 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast…
Mobile App Development Financial Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Mobile App…
Bookkeeping Agency Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Bookkeeping services…
Start Up Company Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking start-up company…
Broilers Poultry Farm – 10 Year Financial Model
Financial Model providing a dynamic up to 10-year financial forecast…
B2B Services Company Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking B2B Services…
Medical Spa (MediSpa) Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Medical Spa…
Medical Clinic Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking private Medical…
Physiotherapy Clinic Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Physiotherapy Clinic…
Fast Food Restaurant Financial Model Template
Maximize fast food financials with our user-friendly financial model template.…
Food Bar Financial Model 5 year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Food Bar…
Restaurant Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Restaurant finances,…
Virtual Reality Software Company Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Virtual Reality…
Budget vs Actual Forecasts 5 Years Excel Template
MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking budget finances. Can be used…
Social Media Marketing Agency Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Social Media…
Affiliate Marketing Agency Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Affiliate Marketing…
Web Hosting Company Finance Model 5 Year 3 Statement
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking web hosting…
5 Year 3 Statement Recycling Centre Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Recycling Centre…
5 Year 3 Statement Construction Company Finance Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking construction company…
5 Year 3 Statement Solar Energy Solutions Company Finance Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Solar Energy…
Digital Advertising Agency Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable 5 Year 3 Statement, MS Excel spreadsheet…
5 Year 3 Statement Virtualization Software Company Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Virtualization Software…
Real Estate Industrial Acquisition Model Single Tenant
This Excel-based tool is tailored for the nuanced analysis of…
5 Year 3 Statement Cyber Security Software Company Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Cyber Security…
Graphic Design Company Finance Model Excel Spreadsheet
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Graphic Design…
Private Equity Fund Financial Projection Model with Distribution Waterfall
Highly versatile private equity fund financial projection model with calculations…
5 Year 3 Statement Private Mental Health Care Centre Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking private Mental…
5 Year 3 Statement Alpaca Farming Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive 3 Statement 5 Year editable, MS Excel spreadsheet…
5 Year 3 Statement Architect Company Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive 5 Year 3 Statement editable, MS Excel spreadsheet…
Swimming School Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Swimming School…
CBD Personal Care Financial Model and Valuation Template
CBD Personal Care Financial Model and Valuation Template, a comprehensive…
EdTech Financial Model and Valuation Template
Empower your EdTech startup with our comprehensive Financial Model, including,…
3 Statement 5 Year SAAS HR Software Development Company Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking SAAS HR…
CRM Software Development Company Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking CRM software…
Pig Farming Finance Model Excel Template
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking pig farming…
3 Statement Indoor Rock Climbing Gym Finance Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Indoor Rock…
3 Statement Car Hire Company Financial Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking car hire…
3 Statement Van Hire Company Finance Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking van hire…
Car Dealership Financial Model and Valuation – Financial Projections
Welcome to the Car Dealership Company Financial Model and Valuation,…
Hospitality (Hotel) Financial Model and Valuation – 10-year Projections
Welcome to the Hospitality (Hotel) Company Financial Model and Valuation,…
Comprehensive 3 – Statement Financial Model for a Midstream Oil and Gas (Refinery with 7- Years Forecast)
This is a 6,000bpd financial model for refinery producing Diesel…
3 Statement Self Storage Company Finance Model
A comprehensive editable, MS Excel spreadsheet for tracking Self Storage…
How Financial Statements Help in Decision Making?

Recall the famous quote from the movie Jerry Maguire, "Show me the money!" It is essentially what financial statements accomplish. They reveal the sources of a company's money, how those funds were utilized, and the current location of those funds. Investors and analysts depend on financial data to assess a company's performance and forecast its future trajectory. Investors and analysts rely on financial data to determine a company's performance and forecast its future trajectory. Financial statements are critical for investors, market analysts, and creditors to gauge a company's financial stability and profitability potential.
A consolidated financial statement is not just a collection of numbers but a mirror reflecting a company's financial situation and performance. They serve as a vital tool for investors, managers, and stakeholders, guiding them through the complexities of decision-making. By analyzing these statements, one can gain invaluable insights into a company's profitability, liquidity, and solvency, enabling informed choices that drive strategic growth and sustainability. Let us explore financial statements' pivotal role in shaping business strategies and ensuring informed decisions.
What are Financial Statements?
Financial statements are detailed written records that outline a company's financial activities and conditions. These documents serve as a formal record of the financial actions of a business, including its revenue, expenses, profitability, and cash flow, over a specific period. They are essential for understanding a company's financial health and making informed business decisions. A consolidated financial statement typically compares data from the current reporting period with the previous one, enabling users to track financial progress and performance over time easily. Presenting information for the latest and prior periods facilitates a clear comparison, helping stakeholders identify trends, assess financial stability, and make predictions about future performance.
The timeframe covered by financial statements can vary. Annual financial statements provide a snapshot of a company's financial position and operations throughout its fiscal year. However, companies also prepare interim financial statements to meet the need for more frequent monitoring and decision-making. These can be issued monthly, quarterly, or semi-annually, offering more immediate data on financial performance and helping in strategic planning and adjustment processes. Financial statements are often subjected to audits by independent accountants or government agencies to ensure their reliability and accuracy. This scrutiny helps verify the information presented, ensuring it adheres to accounting standards and legal requirements. Auditing also serves various purposes, such as fulfilling tax obligations, facilitating financing arrangements, and attracting investors by providing credibility to the company's reported financial status.
The Three Primary Financial Statements
Among the broad types of financial statements are the for-profit and nonprofit statements of financial position. For-profit financial statements offer insights into a company's profitability, liquidity, and financial health. On the other hand, nonprofit financial statements focus on showcasing the organization's stewardship of its resources and its operational effectiveness in achieving its mission without generating profits.
Below the two broad types of financial statements fall the three primary financial statements, including the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. The three primary financial statements provide a comprehensive view of a company's financial health, operational efficiency, and cash management practices.

Balance Sheet
The Balance Sheet provides a snapshot at a particular point in time, detailing the company's assets (what it owns), liabilities (what it owes), and shareholders' equity (the net worth of the company) to illustrate its financial standing and liquidity. Its key components include:
- Assets (what the company owns)
- Liabilities (what the company owes)
- Shareholders' Equity (the remaining interest in the company's assets once all liabilities have been subtracted)
The Balance Sheet equation is: Assets = Liabilities + Shareholders' Equity. This equation represents the foundational principle of double-entry bookkeeping, where each transaction affects at least two accounts to keep the equation balanced. It reflects that a company's assets are funded by borrowing money (liabilities) or contributions from owners and profits retained in the business (shareholders' equity). It is prepared as of a particular date, typically the end of the fiscal year or quarter.
Income Statement
The Income Statement or Profit and Loss Statement details a company's revenues and expenses over a specific period, highlighting net profit or loss to show operational efficiency. It includes key components such as:
- Revenues (income from sales or services)
- Expenses (costs incurred in generating revenue)
- Net Income (the excess of revenues over expenses)
The income statement equation can be summarized as: Net Income = Revenues – Expenses. This equation highlights that a company's net income (or net profit) is the result of subtracting all its expenses from its revenues. It includes all forms of revenues and gains as well as all costs and losses. Unlike the Balance Sheet, which is a snapshot at a point in time, the Income Statement provides a detailed account of a company's financial performance over a specific period, such as a month, quarter, or year, showcasing how the operational and non-operational activities impact the overall profitability.
Cash Flow Statement
The Cash Flow Statement breaks down the company's cash inflows and outflows, offering insight into how it generates and uses its cash over time, which is crucial for understanding its liquidity and solvency. It is divided into three main sections:
- Cash Flows from Operating Activities (day-to-day business operations)
- Cash Flows from Investing Activities (purchase and sale of long-term assets)
- Cash Flows from Financing Activities (transactions involving debt and equity
The cash flow statement equation is structured around the net increase or decrease in cash over a period, which can be represented as: Net Cash Flow = Cash Flows from Operating Activities + Cash Flows from Investing Activities + Cash Flows from Financing Activities. This equation summarizes how cash and cash equivalents change from various business activities during a specific period, reflecting the company's ability to generate cash from its operations, investments, and financing activities. It covers a period similar to the Income Statement.

Other Types of Financial Statements
Financial statements are essential for analyzing a company's financial health and performance, providing a snapshot of its financial activities and condition at a given time. Besides the three primary financial statements, different types of financial statements offer varied perspectives, from asset and liability balances to revenue and expense flows, cash movements, and changes in equity, catering to the diverse needs of stakeholders such as investors, creditors, and management.
Other common for-profit statements of financial position are:
- Actual Financials
- Budgeted Financial Statement
- Multi-Year Financial Statement Projections
- GAAP Financial Statements
- Pro Forma Financial Statements
Other common nonprofit statements of financial position are:
- The statement of financial position
- The statement of activities
- The statement of functional expenses

For-Profit Financial Statements
- Actual Financials: These are financial statements reflecting a business's real financial activities and outcomes within a specific period. Unlike traditional financial statements, actual financials might not adhere to accounting standards rigidly. Based on the collected data, this approach allows for a more flexible representation of a company's financial status, including income, expenses, assets, and liabilities. However, the lack of adherence to a standardized accounting framework might limit the comparability of these financials with those of other entities.
- Budgeted Financial Statements: These statements are forward-looking and represent a company's financial expectations for the upcoming year based on detailed assumptions and calculations. They include revenue projections, expenses, cash flow, and other financial metrics. Budgeted financial statements are essential for internal planning and decision-making, helping businesses set financial goals, allocate resources efficiently, and anticipate potential financial challenges. They are a benchmark against which actual financial performance can be measured, allowing companies to adjust their strategies as needed.
- Multi-Year Financial Statement Projections: These are an extension of budgeted financial statements but extend over a longer horizon, typically spanning multiple years into the future. Based on financial modeling, these projections attempt to predict how a business will perform financially, considering market trends, economic conditions, and strategic initiatives. Multi-year projections are crucial for long-term strategic planning, investment decisions, and, in some cases, to secure funding from investors or lenders by demonstrating the future financial potential of the business.
- GAAP Financial Statements: These financial statements are prepared using generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP), a set of rules and guidelines designed to ensure that financial reporting is transparent, consistent, and comparable across different entities. Adherence to GAAP ensures that stakeholders, including investors, regulators, and analysts, can rely on the financial statements to make informed decisions, as it provides a common language for financial reporting.
- Pro Forma Financial Statements: These are financial statements that are either preliminary versions of actual financials pending final adjustments or hypothetical scenarios that illustrate what a company's financial situation could look like under certain conditions. Pro forma financials are often used to show the effects of significant upcoming events such as mergers, acquisitions, or major changes in capital structure. When used as preliminary financials, they provide an early view of a company's performance, subject to revisions. As hypothetical projections, they help stakeholders understand potential financial outcomes based on specific assumptions, aiding in strategic planning and decision-making.
Nonprofit Financial Statements
- The Statement of Financial Position in a nonprofit context is akin to a balance sheet for a for-profit entity, detailing an organization's assets, liabilities, and net assets at a specific point in time, offering a snapshot of its financial health.
- The Statement of Activities is equivalent to an income statement, showing the revenue, expenses, and changes in net assets over a period, highlighting how funds are generated and used to pursue the organization's mission.
- The Statement of Functional Expenses breaks down expenses by both their nature (such as salaries, rent, utilities) and function (program services, fundraising, and administration), providing a detailed view of how resources are allocated across different activities, ensuring that donors, grant makers, and other stakeholders understand how the nonprofit uses its resources to achieve its goals and objectives.
What Are the Benefits of Financial Statements?
Financial statements are crucial for clearly and accurately representing a company's financial position and performance over time. They benefit stakeholders by facilitating informed investment decision-making and financial planning and understanding the company's profitability, liquidity, and financial stability.
- Assists in Obtaining Financing: Financial statements are crucial for businesses seeking different funding sourcesfrom banks, investors, or other financial institutions. These documents provide a comprehensive view of the company's financial health, including its profitability, cash flow, and overall financial stability. By presenting detailed financial information, businesses can demonstrate their ability to generate profits and manage expenses effectively, making them more attractive to potential financiers. This transparency helps lenders and investors assess the risk of financing the business, facilitating decision-making.
- Bolster Internal Control: Financial statements play a vital role in strengthening internal controls within an organization. They offer a systematic record of financial transactions, assets, and liabilities, which can be regularly reviewed and audited. This process ensures accuracy in financial reportingand helps detect and prevent errors, fraud, or mismanagement of funds. By establishing internal solid controls through regular financial statement analysis, companies can safeguard assets, ensure financial integrity, and comply with financial regulations and standards.
- Facilitates Performance Review: Regular preparation and analysis of financial statements allow businesses to monitor their performance over time. By comparing current financial data with previous periods or benchmarks, companies can identify trends, measure progress toward financial goals, and pinpoint areas of improvement. This review helps assess the effectiveness of business strategies, operational efficiency, and cost management practices. Ultimately, it enables management to make informed decisions to enhance profitability and growth.
- Helps in Managing Risks: Financial statements provide valuable insights into various financial and operational risks facing a business. Companies can identify potential financial vulnerabilities by analyzing revenue streams, expense patterns, debt levels, and liquidity. This analysis aids in developing strategies to mitigate risks, such as diversifying income sources, optimizing inventory levels, or restructuring debt. Effective risk management based on financial statement analysis helps ensure the long-term sustainability of the business.
- Steers Strategy Development: The strategic planning process benefits greatly from the insights gained through financial statement analysis. By understanding the company's financial strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, management can develop strategic objectives that are both realistic and ambitious. Financial statements help set financial targets, allocate resources efficiently, and prioritize initiatives that drive growth and profitability. They serve as a foundation for devising strategies that align with the company's financial health and market position, guiding the business toward achieving its long-term goals.

How are Financial Statements Prepared?
Preparing financial statements is a systematic process that involves several key steps to ensure accuracy and compliance with accounting standards. Here's an explanation of each step:
- Collect all pertinent financial information: This first step involves gathering all relevant financial data that will be used to prepare the financial statements. This data includes, but is not limited to, bank statements, receipts, invoices, and records of financial transactions. The aim is to ensure that all financial activities conducted during the period in question are accounted for, providing a complete picture of the entity's financial status.
- Classify and arrange the data: Once all the financial data is collected, it must be organized meaningfully. It involves classifying the data into different categories: revenues, expenses, assets, liabilities, and equity. This classification is crucial for preparing financial statements as it allows for a systematic data analysis. The classified data is then arranged according to the structure of the financial statements, facilitating the subsequent steps in the preparation process.
- Prepare initial financial reports: With the data classified and arranged, the next step is to prepare the initial drafts of the financial statements. It typically includes the balance sheet, income, and cash flow statement. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the entity's financial position at a specific time, showing assets, liabilities, and equity. The income statement shows the entity's financial performance over time, detailing revenues and expenses to arrive at a net profit or loss. The cash flow statement outlines the inflows and outflows of cash, highlighting how the entity's cash position has changed over time.
- Review and adjust data discrepancies: After the initial financial statements are drafted, they must be reviewed for accuracy and consistency. This review process may uncover differences or errors in the data, which must be adjusted to ensure that the financial statements accurately reflect the entity's financial position and performance. Adjustments may include correcting errors, reallocating misclassified transactions, or making adjustments for accruals and deferrals to comply with the accrual basis of accounting.
- Summarize the report using charts & graphs: The final step in preparing financial statements involves summarizing the data in a visually appealing and easily understandable format. Charts and graphs can highlight key financial metrics and trends, making it easier for stakeholders to digest and interpret the financial information. This visual summary complements the detailed financial statements, providing a quick overview of the entity's financial health and performance.
Each of these steps is critical to ensuring that financial statements are accurate, complete, and compliant with accounting standards, thereby providing valuable information to stakeholders for decision-making.

Streamline Financial Decisions with Financial Statement Templates in Excel
Financial statements are pivotal tools in business and finance, acting as a window into a company's financial health. They mainly consist of the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement, each providing unique insights into a company's financial performance. By analyzing these statements, decision-makers can assess profitability, understand cash flows, evaluate the balance between assets and liabilities, and make informed decisions. This informed decision-making is crucial for strategic planning, investment choices, identifying areas for improvement, and ensuring the financial stability and growth of the business.
Streamlining financial decisions becomes significantly more efficient using financial statement templates in Excel. These templates offer a structured and standardized way to organize financial data, automate calculations, and visualize financial metrics through charts and graphs. By leveraging Excel's powerful features, such as pivot tables, formulas, and conditional formatting, users can quickly analyze trends, compare financial performance over different periods, and forecast future financial scenarios using financial statement templates in Excel. They save time, enhance accuracy, and provide a clear basis for making strategic financial decisions. With the help of financial statement templates in Excel, businesses can more easily monitor their financial status, plan for the future, and respond to changing financial conditions with agility and confidence.